P. 1 cover
DID YOU KNOW THAT
YOU CAN LEARN PHYSICS
THROUGH VOLLEYBALL?
It looks at the following questions:
What 2
forces help the ball go up?
What 2
forces help the ball go down?
What’s
the physics of jumping?
What are
parabola and trajectory, and
what do
they have to do with volleyball?
http://sportscience-kathy.blogspot.com
GATEWAY TO SCIENCE:
SPORTS AND GAMES
Quincy, Mass.
P. 2 inside left
What
are the 3 laws of motion?
How
do they apply to volleyball?
1st Law –
Inertia
The
tendency of a moving object – like a volleyball – to stay in motion, until
acted upon by another object or a force (like gravity or friction).
2nd Law – Force
F = m × a or F = m · a What does
it mean?
The
ball is made of mass. The amount
of Force depends on how hard you hit the mass of the ball and how fast
it accelerates –
The Action
3rd Law – The
Reaction
Every
Action has an equal and opposite Reaction.
The
pace of the game usually depends on the Force (the Action):
↓
Slower pace
means less Force is used.
Faster pace means more Force is used.
P. 3 inside center
WHAT KIND
OF FORCES ARE INVOLVED IN THE BALL GOING UP AND DOWN?
This shows you how 4
forces work on the ball – in pairs and against each other.
__________________
D. FRICTION aka DRAG C. GRAVITY
Force that slows ↓ the motion Force that pulls things down ↓
of things It is always present!
A. THRUST ↑ B. LIFT ↑
Uses the force of your energy Upward force that opposes pull of gravity
___Source: Ref. 2, Van Voorst___
P. 4 inside right:
What are parabola and trajectory – and what do they have to do with volleyball?
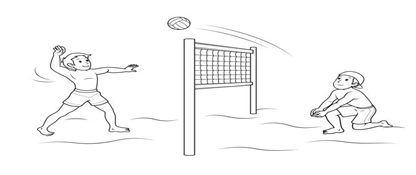
Θ Part of a circle is
called an arc, the shape of the path
that the ball takes as it travels through the air.
Θ We also use the word parabola
to describe specifically the shape made by the ball. Both arc and parabola are words used in
geometry, focusing on shape.
Θ There’s another word that’s also about shape, but more than that, it’s about motion too. That word is trajectory. Trajectory is the path taken by a moving object – a ball that has been thrown.
Θ Here are other -ject words: project – object – reject – eject – inject
P. 5 back, left
MORE QUESTIONS!
Trivia Question
Who invented volleyball?
Answer
William G. Morgan, an American, invented volleyball in 1895. He raised a net used for tennis, and players used their hands to volley the ball back and forth over the net.
(Ref. 1, Doeden)
Question
When you jump up and down, how does the 3rd law of motion apply to this?
Answer
Remember:
Every action has an equal and opposite reaction. When you jump, you apply force to the ground with your feet. The ground returns the force, and you are pushed into the air.
The harder you push,
the higher you jump!
(Ref. 2, VanVoorst)
____________________
Sports and games are the
gateway to science,
and YOU hold the key!
Volleyball
…
is just one of endless ways to gain an understanding of physics and geometry.
I hope this leaflet introduces you to
seeing things you never saw before – or wondered about but
just didn't know where to start.
Physics and geometry come into play in every activity and event going on around us.
Knowing how things work can add to your performance and to your fun. So give it a try. How?
•
Start
with the information here
•
You may
not understand everything in it right away, but for now, use what you do understand
•
Do
an online search of your own
•
See what
books or videos
your library has
•
Share
them with friends, your class, your team, your scout troop
•
Read
my blog and tell others:
sportscience-kathy.blogspot.com
Thank you! Kathy Hogan
REFERENCES
(1)
Volleyball by Matt Doeden, Amicus Publishing, Mankato, MN, 2016
(2) STEM in the Summer Olympics: The Science Behind Volleyball
by Jenny Fretland-VanVoorst, Pogo Books/Jump!, Minneapolis, MN, 2020

